A geofence is a geometry, most commonly a polygon, used for spatial proximity analysis. For example, an Incident Detector Processor might be configured to detect when the coordinates of a received event are inside or outside a specified set of geofences. A GeoTagger Processor might be configured to include the name of a geofence when an event's geometry is discovered to be inside a geofenced area.
Administrators can create geofences from existing feature datasets (typically polygon feature classes). The following are a few items to remember when working with geofences in GeoEvent Server:
- Individual geofences must have a unique name. When importing geofences from a feature service, you will be asked for the field that contains each feature's name; ideally, this should be a string field type.
- Geofences are organized within named categories. When importing geofences from a feature service, you have the option to either specify the field that contains the category name or enter a literal string and import geofences into the named category.
- Administrators can rename individual geofences or move them into another category by clicking Edit to the right of the listed geofences in GeoEvent Manager.
- GeoEvent Server can update its known set of geofences based on the contents of a published feature service. Synchronization with the feature service is conducted periodically based on a refresh interval specified by an administrator; every 15 minutes is the system default. Although the refresh interval can be configured to occur as frequently as once per second, this type of rapid synchronization should be avoided when working with feature services. Factors such as network latency and size of the data can impede a feature service's ability to return data in the configured refresh interval. As a result, geofences may not update in the expected time frame. For example, if the refresh interval has been set to thirty seconds for a feature service that takes a minute to provide a response, geofences will update approximately once every minute and a half.
- GeoEvent Server can add and update its known set of geofence based on the data received from a stream service. Consider employing a stream service for geofence synchronization as an alternative to feature services when accelerated geofence synchronization is needed. Using WebSocket technology, stream services can be used to add and update geofences in a near-instantaneous manner. No refresh interval is required.
- Geofences are included in the configuration of a filter or processor in a GeoEvent Service to support spatial proximity analysis. Examples include spatial filters for filter elements as well as the Incident Detector Processor and GeoTagger Processor.
View available geofences by browsing to Site > GeoEvent > GeoFences in GeoEvent Manager.
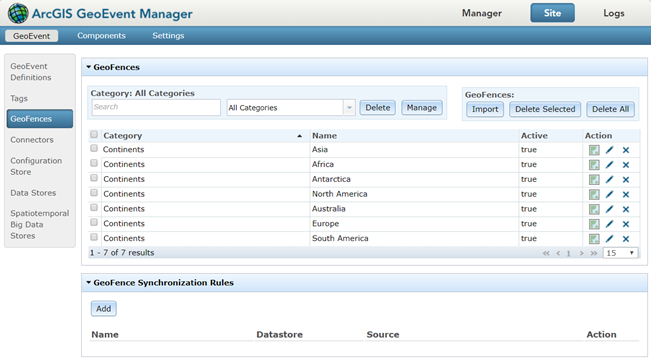
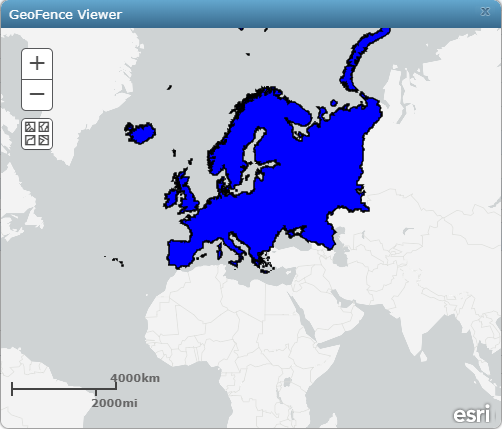
Additionally, data administrators can browse to Site > GeoEvent > GeoFences to visualize available geofences using the GeoFence Viewer in GeoEvent Manager.
The Introduction to GeoEvent Server tutorial contains exercises illustrating how to import geofences from a feature dataset and how to configure synchronization so GeoEvent Server will automatically update its geofences based on the contents of a published feature service. Access the tutorial from GeoEvent Server tutorials.