 The Remap Values tool changes the cell values of the input raster to new values.
The Remap Values tool changes the cell values of the input raster to new values.
Workflow diagram
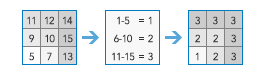
Examples
- Given a temperature raster dataset, change ranges of temperature values into zones 1, 2, and 3 to designate heat zones.
- Given a land cover dataset, change the values of classes 16 and 21 into a new class with value 23, effectively merging the classes into a new one.
Usage notes
This tool allows you to change or reclassify the pixel values of the raster data. Pixel values are remapped by specifying a range of pixel values to map to an output pixel value. The output pixel value can be a valid value or a NoData value, which are pixels that do not have a known value associated with them.
When specifying the values to be remapped, the minimum value is inclusive (included in the values to be remapped) and the maximum value is exclusive (not included in the values to be remapped).
| Minimum (inclusive) | Maximum (exclusive) | Values that are converted to the output value |
|---|---|---|
1 | 10 | 1–9 |
10 | 20 | 10–19 |
50 | 51 | 50 |
The order of the ranges specified in the table is also important. The top row of the table is processed first, and then the row below is processed. The two tables below show how the same value ranges will produce different results due to the order of the table rows.
Example 1
| Minimum (inclusive) | Maximum (exclusive) | Values that are converted to the output value |
|---|---|---|
1 | 15 | 1–14 |
10 | 30 | 15–29 |
30 | 40 | 30–39 |
Example 2
| Minimum (inclusive) | Maximum (exclusive) | Values that are converted to the output value |
|---|---|---|
10 | 30 | 10–29 |
1 | 15 | 1–9 |
30 | 40 | 30–39 |
Both rules are employed to reorder the values. Since each row is processed from top to bottom, these values take precedence when determining the output, even when the same ranges are used.
If Use current map extent is checked, only the pixels that are visible in the current map extent will be analyzed. If unchecked, the entire input imagery layer will be analyzed.
The parameters for this tool are listed in the following table:
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Choose input data to remap values | The input data that will have its values remapped. |
| Remap pixel values to new values | Enter a range of values by specifying a minimum and maximum value, and then assign an output value or a NoData value to the specified range. To remap a new range of values, click Add, which adds a row. Click each value to edit the table to the ranges and remapped value you need. When you specify the value ranges, there are two important rules that are employed:
|
| Result layer name | The name of the layer that will be created in My Content and added to the map. The default name is based on the tool name and the input layer name. If the layer already exists, you will be prompted to provide another name. You can specify the name of a folder in My Content where the result will be saved using the Save result in drop-down box. |
Environments
Analysis environment settings are additional parameters that affect a tool's results. You can access the tool's analysis environment settings by clicking the gear icon  at the top of the tool pane.
at the top of the tool pane.
This tool honors the following Analysis Environments:
- Output coordinate system—Specifies the coordinate system of the output layer.
- Extent—Specifies the area to be used for analysis.
- Snap Raster—Adjusts the extent of the output so it matches the cell alignment of the specified snap raster layer.
- Cell size—The cell size to use in the output layer.
- Mask—Specifies a mask layer, where only the cells that fall within the mask area will be used for analysis.
- Resampling method—The method to use to interpolate pixel values.
- Recycle interval of processing workers—Defines how many image sections to process before restarting worker processes.
- Parallel processing factor—Controls the raster processing CPU or GPU instances.
- Number of retries on failures—Defines how many retries a worker process will attempt when there is random failure processing a job.
Similar tools and raster functions
Use Remap Values tool to reclassify cell values into new values in an imagery layer. Other tools may be useful in solving similar problems.
Map Viewer Classic analysis tools and raster functions
Use the Remap raster function to perform the same operation as the Remap Values tool. Chain this function with other functions for a custom workflow.
ArcGIS Pro analysis tools and raster functions
The Reclassify geoprocessing tool is available in the Spatial Analyst and the 3D Analyst toolboxes. Other tools in the Reclass toolset perform similar operations.
Remap is also available as a raster function.