Available with Image Server
Calculates statistics on values of a raster within the zones of another dataset.
A zone is defined as all areas in the input that have the same value. These areas do not have to be contiguous. When the zone and value inputs are both rasters of the same resolution, they will be used directly. If the resolutions are different, an internal nearest neighbor resampling is applied to make the resolutions match to that of the coarser input before the zonal operation is performed.
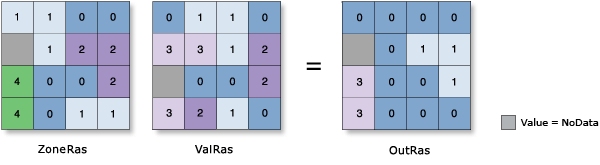
For more information, see How Zonal Statistics works topic.
This is a global raster function.
Notes
The Zone Raster must be an integer raster input. If you have feature zones, first convert the feature data into a raster with the Rasterize Features function before using it in this function. Set the cell size and snap raster environment to the Value Raster when converting the feature data to raster.
When specifying the input zone data, the default Zone Field will be the first available integer or text field.
To calculate circular statistics, check the Calculate Circular Statistics parameter, and specify a Circular Wrap Value.
The supported statistics type depends on the data type of the Value Raster, and the statistics calculation type specified by the Calculate Circular Statistics parameter.
The Value Raster can be either integer or floating point. If the data type is integer, arithmetic statistics calculation supports Mean, Majority, Majority count, Majority percentage, Maximum, Median, Minimum, Minority, Minority count, Minority percentage, Percentile, Range, Standard deviation, Sum, and Variety statistics types; circular statistics calculation supports Mean, Majority, Minority, Standard deviation, and Variety statistics types.
If the Value Raster data type is float, arithmetic statistics calculation supports Mean, Maximum, Median, Minimum, Percentile, Range, Standard deviation, and Sum statistics types; circular statistics calculation supports Mean and Standard deviation statistics types.
The data type of the output is dependent on the zonal calculation being performed and the input Value Raster type. See How Zonal Statistics works for more information.
For Majority and Minority calculations, when there is a tie, the output is the lowest of the tied values.
Parameters
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
Zone Raster (Required) | The dataset that defines the zones. The zones can be defined by an integer raster. |
Zone Field (Required) | The field that contains the values that define each zone. It can be an integer or a string field of the zone raster. |
Value Raster (Required) | The raster that contains the values on which to calculate a statistic. |
Statistics Type | Specifies the statistic type to be calculated.
|
Percentile Value | The percentile to calculate. The default is 90, for the 90th percentile. The value can range from 0 through 100. The 0th percentile is essentially equivalent to the Minimum statistic, and the 100th percentile is equivalent to Maximum. A value of 50 will produce essentially the same result as the Median statistic. This option is only available if the Statistics type parameter is set to Percentile. |
Percentile Interpolation Type | Specifies the method of interpolation to be used when the specified percentile value lies between two input cell values from the input value raster.
This option is only available if the Statistics type parameter is set to Median or Percentile. |
Calculate Circular Statistics | Specifies how the statistics type will be calculated.
|
Circular Wrap Value | The highest possible value (upper bound) in the cyclic data. It is a positive number, with a default value of 360. This value also represents the same quantity as the lowest possible value (lower bound). This parameter is applicable only when circular statistics is calculated. |
Ignore NoData in Calculations | Specifies whether NoData values in the Value Raster will influence the results of the zone that they fall within.
|
Process as Multidimensional | Specifies how the input rasters will be processed if they are multidimensional.
|