Name and description
A meaningful name and description for the parameters helps your clients understand and provide appropriate values for the parameter. By default, the Service Editor copies the description of the parameter from the tool's item description.
Type
The parameter type defines whether the
client must supply a value for the task to execute successfully. In the Service Editor, you can only change optional parameters to required. To change a required parameter to an optional parameter, you'll need to exit the Service Editor, edit the properties of your tool, and run the tool again to create a new result.
Input mode
The Input mode determines how clients will input features to your task. There are three choices, described in detail below.
User defined value
In this mode, the client will create their own table rows as input to the task parameter. The client can construct these rows using any technique suitable to their application. For ArcGIS for Desktop clients, the Record Set data type is used to construct table rows for geoprocessing tasks.
Schema
The Schema is a list of fields (attributes) that need to be supplied by the client when they construct the features for input to the task. This list of fields is same as the table you used as input to the tool that created the result. 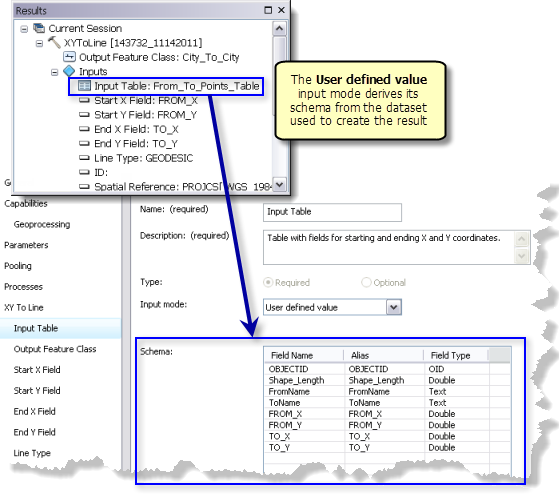
Since this is a list of fields that need to be supplied by the client, you need to review the list carefully. Are there fields that aren't required? If so, you should either delete them or document that they are optional in the parameter's Description. Use the Description to describe how the fields affect task execution.
Note:
The schema cannot be modified in the Service Editor. See Feature and table schemas for task parameters for methods to edit the schema.Include records
If Include records is checked, the table rows used to create the result will be included as part of the parameter definition. That is, the parameter is prepopulated with rows.
Use this option if you want to start with a set of table rows that the client can add, and remove rows and edit attributes. For example, you may have a site selection task and you want the client to enter a table of weights for 12 selection criteria. There is one row for each criteria, and by including records, the client receives the table with 12 rows and edits the weights for each criteria; they don't have to add or remove any records.
Choice list
Use the Choice list input mode when you want the client to choose one (or more) tables as input. The list of tables in the Service Editor is populated from the tables in the current map document. Check the box next to the table or tables the client can choose as input.
Note:
You cannot add new tables or change their names in the Service Editor. Remove your task from the Service Editor, add or rename tables in the table of contents, then click Add Result  to add the result you removed previously. You'll see the changes you made to the table of contents.
to add the result you removed previously. You'll see the changes you made to the table of contents.
Default value
The default value is the value of the parameter used to create the result. If the client fails to specify a value for the parameter, the task executes using the default value.
Note:
You cannot change the default value in the Service Editor. To change the value, remove the result from the Service Editor, create a new result with the values you want to have as the default values, then click Add Result  to add the new result.
to add the new result.
Constant value
Use the Constant value mode when you want the task parameter to be fixed to a constant value.
- The value used for the Constant value is always the parameter value used to create the result. To change this value, you must create a new result with the desired value and publish the new result.
- Parameters with an input mode of Constant value do not become task parameters in the published task since clients cannot change their value.
- In this mode, the table or tables become project data used by the task.