In the workflow described below, three Esri Amazon Web Services (AWS) CloudFormation templates are used to create a stand-alone ArcGIS Server site and an enterprise geodatabase registered with the ArcGIS Server site. Using this workflow, you can set up a deployment architecture as shown in the following diagram:
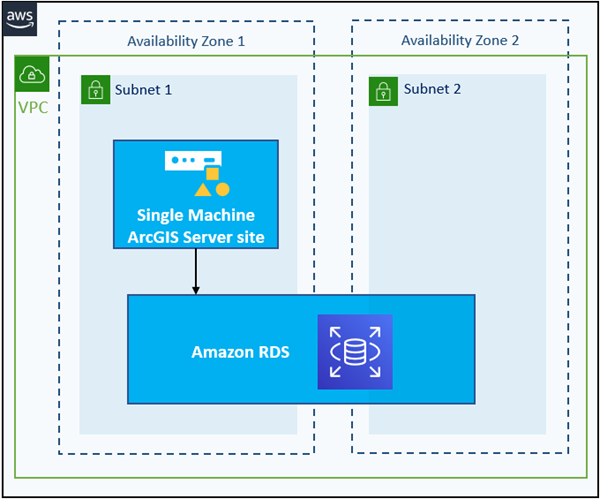
Follow these steps to create the architecture depicted above.
- Use the Esri AWS CloudFormation template for a VPC with two public subnets to create an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
- Use the single-machine ArcGIS Server site Esri CloudFormation template to create an ArcGIS Server site on one Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instance.
Tip:
- Use an ArcGIS GIS Server license file.
- For the VPC ID and SubnetID input parameters, use the output values from the stack created in step 1.
- If you will create a geodatabase in Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) for SQL Server, the ArcGIS Server site must run on a Microsoft Windows instance.
- Use one of the following Esri CloudFormation templates to create an enterprise geodatabase in the applicable database service type:
Tip:
- For the VPC ID and SubnetID input parameters, use the output values from the stack created in step 1.
- For the Site Administrator User Name and Site Administrator User Password input parameters, use the same values that you used when creating the ArcGIS Server site in step 2.
- For the ArcGIS Server Instance ID input parameter, choose the EC2 instance ID created by the CloudFormation template you used in step 2.
- If you created an ArcGIS GIS Server site, you can add the geodatabase as a registered database, which means it will store source data.